 MapReduce原理
MapReduce原理
# MapReduce 原理
通过前面的 Hadoop 序列化 此处难以理解
# InputFormat 数据输入
# FileInputFormat 切片源码



# CombineTextInputFormat 切片机制
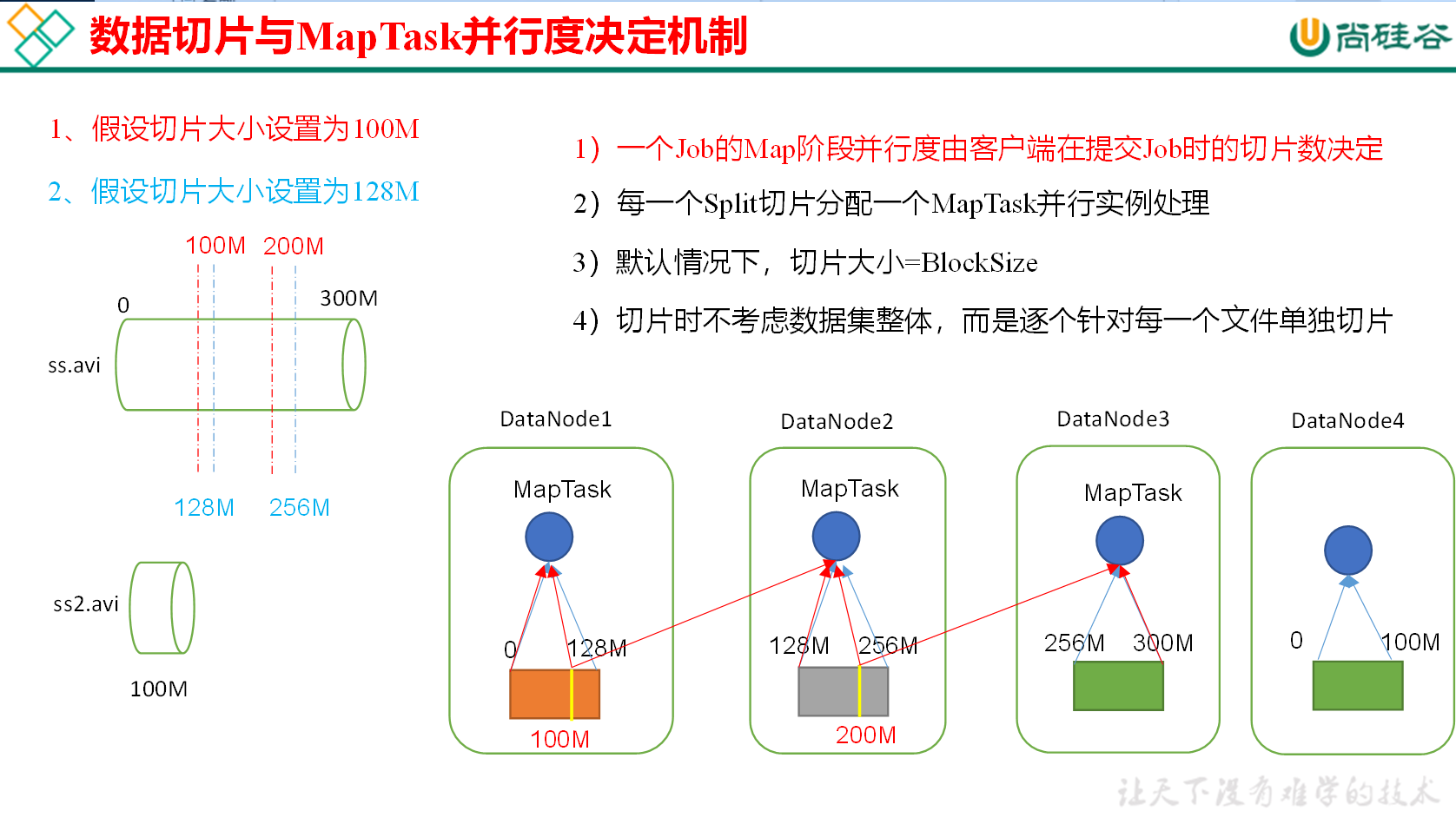
框架默认的 TextInputFormat 切片机制是对任务按文件规划切片,不管文件多小,都会是一个单独的切片,都会交给一个 MapTask,这样如果有大量小文件,就会产生大量的 MapTask,处理效率极其低下。

# 自定义 InputFormat
Driver
package com.inputformat;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.BytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.SequenceFileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyInputDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(MyInputDriver.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(BytesWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(BytesWritable.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(MyInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:/input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:/output"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
InputFormat
package com.inputformat;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.BytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<Text, BytesWritable> {
/**
* 返回一个自定义RecordReader
* @param inputSplit
* @param taskAttemptContext
* @return
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
public RecordReader<Text, BytesWritable> createRecordReader(InputSplit inputSplit, TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return new MyRecordReader();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
RecordReader
package com.inputformat;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.BytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import java.io.IOException;
//负责将整个文件转化成一组Key Value对
public class MyRecordReader extends RecordReader<Text, BytesWritable> {
//文件是否读完 默认为false
private boolean isRead;
//键值对
private Text key=new Text();
private BytesWritable value= new BytesWritable();
FSDataInputStream inputStream;
FileSplit fs;
/**
* 初始化方法 一般执行一些初始化操作
*
* @param inputSplit
* @param taskAttemptContext
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
public void initialize(InputSplit inputSplit, TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//开流
fs = (FileSplit) inputSplit;//强转为实现子类
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(taskAttemptContext.getConfiguration()); //获取config对象
inputStream = fileSystem.open(fs.getPath());//获取路径
}
/**
* 读取下一个键值对 是否存在
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (!isRead){
//读取这个文件
//填充key
key.set(fs.getPath().toString()); //key路径
//value
byte[] buffer = new byte[(int) fs.getLength()];
value.set(buffer,0,buffer.length);
//标记文件读完
isRead = true;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
获取当前key
*/
@Override
public Text getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return key;
}
//获取当前value
@Override
public BytesWritable getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return value;
}
/**
* 显示进度
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
public float getProgress() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return isRead ? 0 : 1;
}
/*
关闭方法
*/
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
IOUtils.closeStream(inputStream); //关流
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
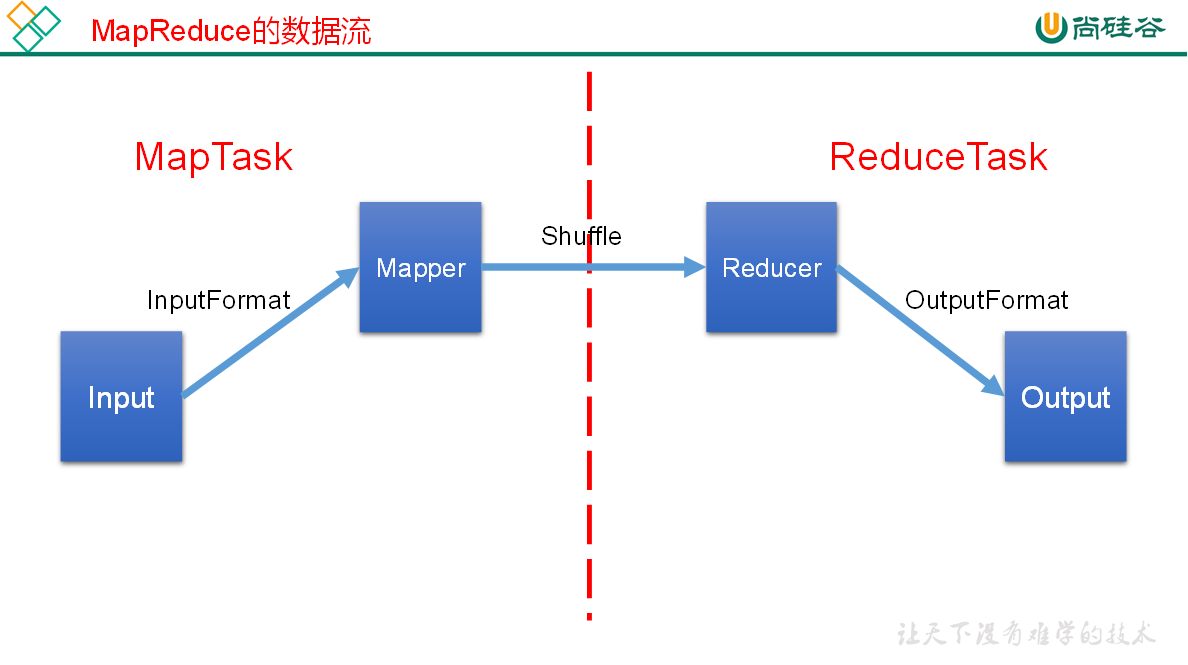
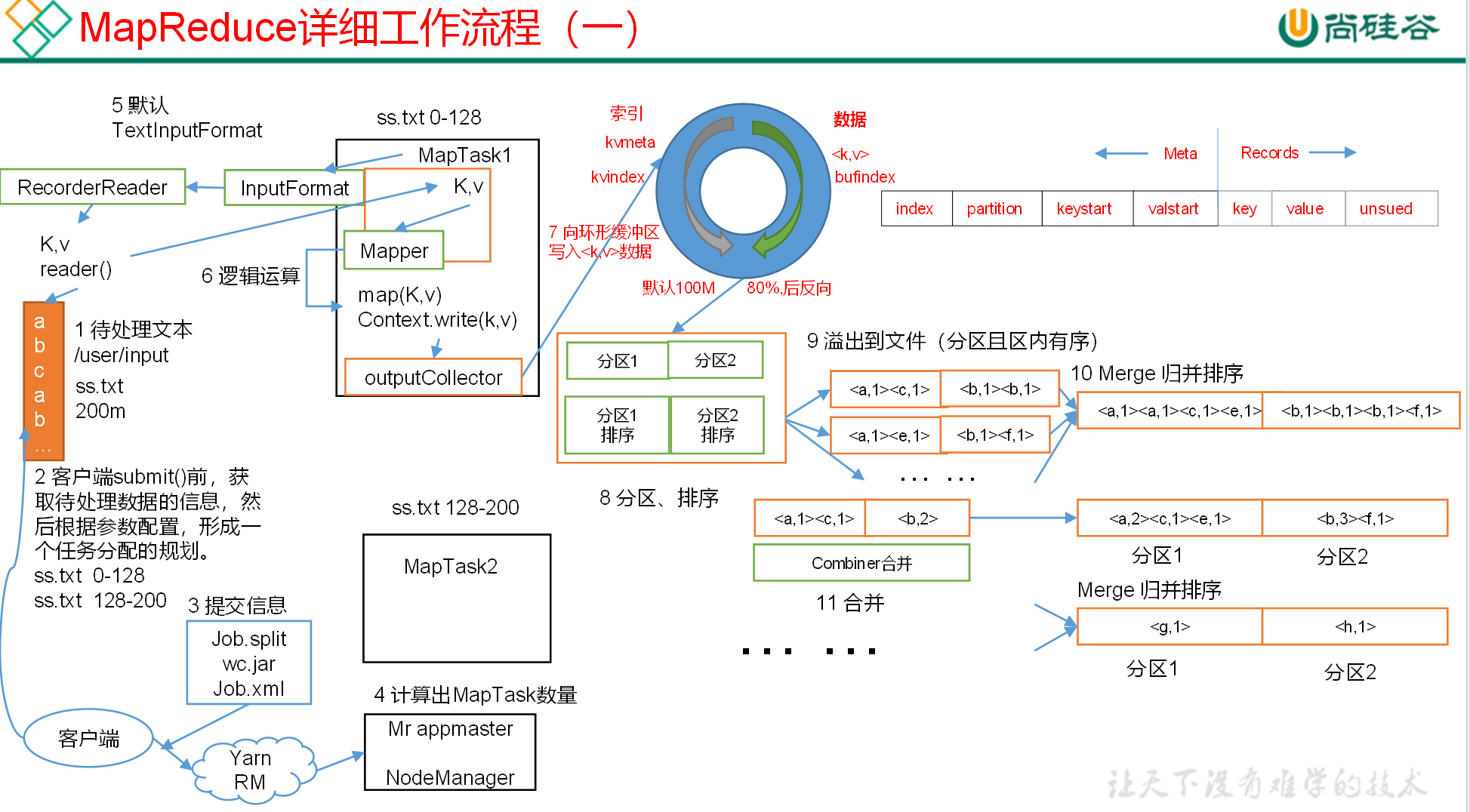
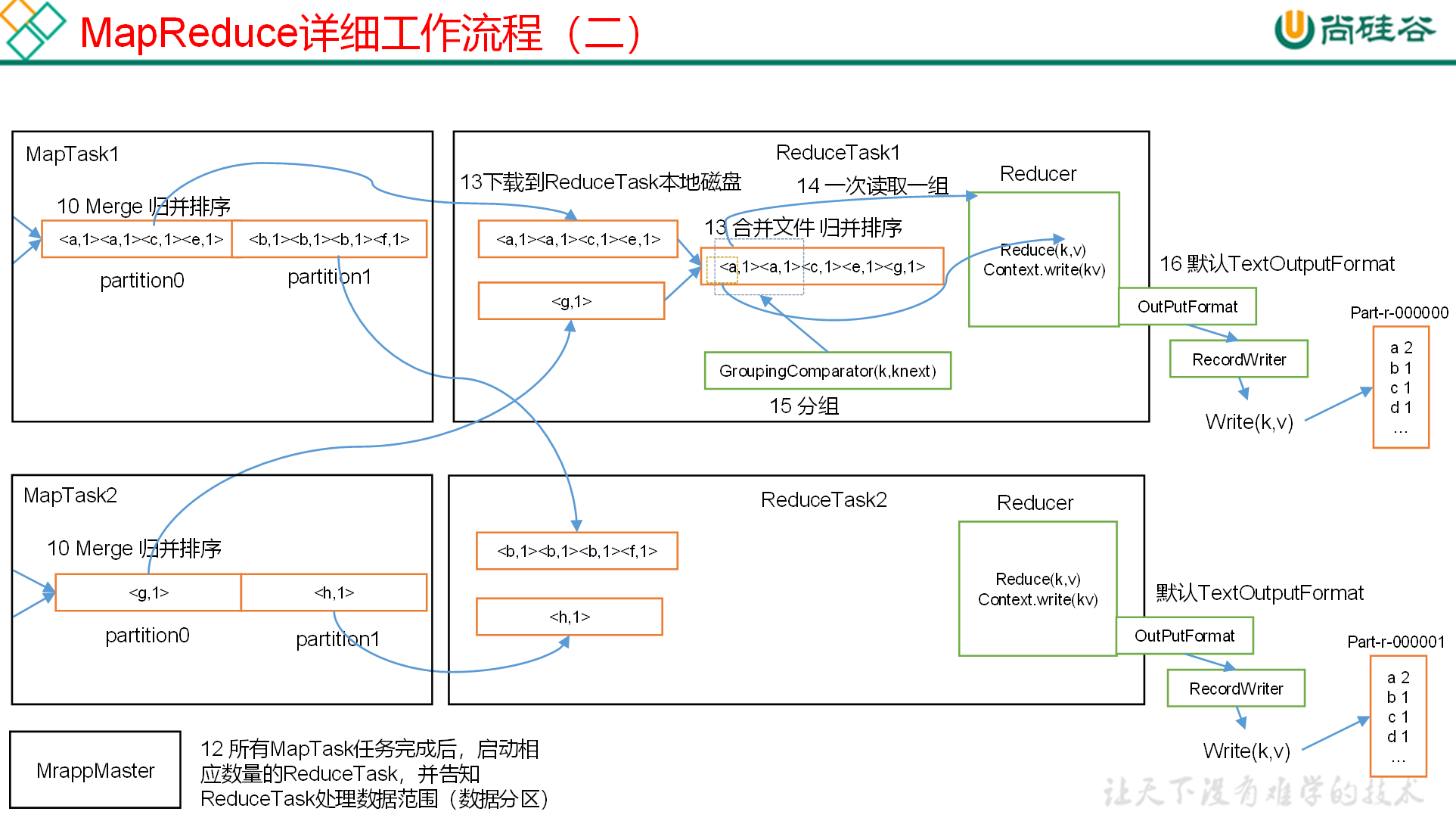
# Shuffle (混洗) 整理数据
MapReduce 框架会确保每一个 Reducer 的输入都是按 Key 进行排序的。一般,将排序以及 Map 的输出传输到 Reduce 的过程称为混洗(shuffle)。每一个 Map 都包含一个环形的缓存,默认 100M,Map 首先将输出写到缓存当中。当缓存的内容达到 “阈值” 时(阈值默认的大小是缓存的 80%),一个后台线程负责将结果写到硬盘,这个过程称为 “spill”。Spill 过程中,Map 仍可以向缓存写入结果,如果缓存已经写满,那么 Map 进行等待。
Map 方法之后,Reduce 方法之前的数据处理过程称之为 Shuffle。
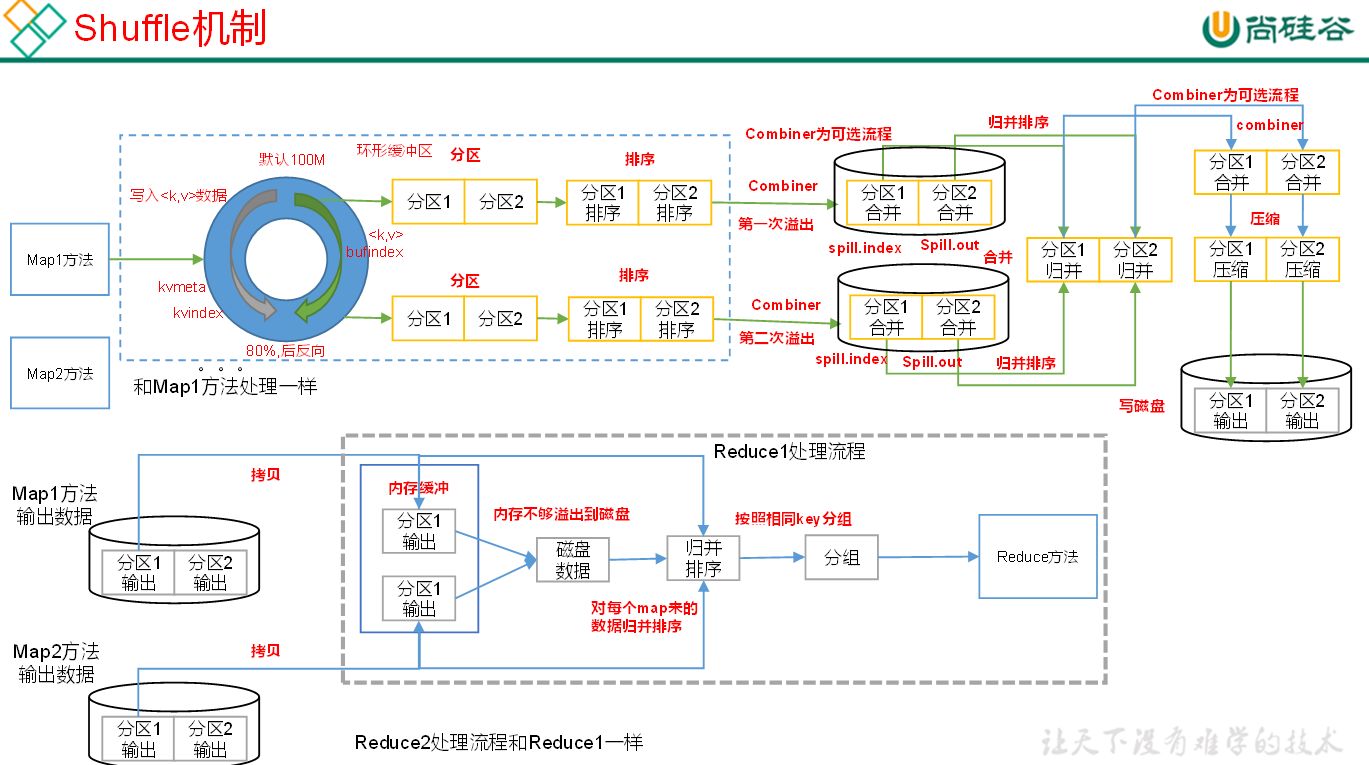
Shuffle 将 map 中无序的键值对,分区 排序 归并后输出给 Reduce
Shuffle 阶段数据是存放在内存 (栈) 中,如果数据写满了缓冲区,则会进行分区 并排序 然后进行归并排序 并且写入磁盘的操作,以释放缓冲区 让新数据进入缓冲区
一次排序比多次排序效率要高 因为归并次数越多效率下降 但如果是数据集庞大 我们只有牺牲时间来换取空间
# Partition 分区
实体类
package com.flow;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FlowBean implements Writable {
private long upFlow;
private long downFlow;
private long sumFlow;
@Override
public String toString() {
return upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow;
}
public void set(long upFlow, long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
this.upFlow = upFlow;
this.sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow;
}
public long getUpFlow() {
return upFlow;
}
public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) {
this.upFlow = upFlow;
}
public long getDownFlow() {
return downFlow;
}
public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
}
public long getSumFlow() {
return sumFlow;
}
public void setSumFlow(long sumFlow) {
this.sumFlow = sumFlow;
}
/**
* 将对象数据写出到框架指定地方 序列化
*
* @param dataOutput 数据的容器
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeLong(upFlow);
dataOutput.writeLong(downFlow);
dataOutput.writeLong(sumFlow);
}
/**
* 从框架指定地方读取数据填充对象 反序列化
*
* @param dataInput
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
//读写顺序要一致
this.upFlow = dataInput.readLong();
this.downFlow = dataInput.readLong();
this.sumFlow = dataInput.readLong();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
分区类
package com.partitioner;
import com.flow.FlowBean;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, FlowBean> {
/**
* 对每一个键值对 返回对应的分区号
*
* @param text 手机号
* @param flowBean 流量
* @param numPartitions
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, FlowBean flowBean, int numPartitions) {
switch (text.toString().substring(0, 3)) { //根据手机号前3位
case "136":
return 0;
case "137":
return 1;
case "138":
return 2;
case "139":
return 3;
default:
return 4;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
驱动类
package com.partitioner;
import com.flow.FlowBean;
import com.flow.FlowMapper;
import com.flow.FlowReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class NewFlowDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(NewFlowDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(FlowMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(5); //设置分区数/并行数
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class); //设置分区类
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("file:///d:/input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("file:///d:/output"));
boolean completion = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(completion ? 0 : 1);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# WritableComparable 排序
WritableComparable 是 MapReduce 中默认的排序接口 实现类为 WritableComparator
MapTask 和 ReduceTask 均会对数据按照 key 进行排序 hadoop 的默认行为 默认排序为字典顺序排序 底层为快速排序
如果要重写排序方法 则让实体类继承 WritableComparable 接口 并实现 compareTo 方法
实现类
package com.compare;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
//实现WritableComparable接口
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean> {
private long upFlow;
private long downFlow;
private long sumFlow;
@Override
public String toString() {
return upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow;
}
public void set(long upFlow, long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
this.upFlow = upFlow;
this.sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow;
}
public long getUpFlow() {
return upFlow;
}
public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) {
this.upFlow = upFlow;
}
public long getDownFlow() {
return downFlow;
}
public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
}
public long getSumFlow() {
return sumFlow;
}
public void setSumFlow(long sumFlow) {
this.sumFlow = sumFlow;
}
/**
* 将对象数据写出到框架指定地方 序列化
*
* @param dataOutput 数据的容器
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeLong(upFlow);
dataOutput.writeLong(downFlow);
dataOutput.writeLong(sumFlow);
}
/**
* 从框架指定地方读取数据填充对象 反序列化
*
* @param dataInput
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
//读写顺序要一致
this.upFlow = dataInput.readLong();
this.downFlow = dataInput.readLong();
this.sumFlow = dataInput.readLong();
}
//比较器
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean o) {
// if (this.sumFlow < o.sumFlow) {
// return 1; //降序
// } else if (
// this.sumFlow == o.sumFlow
// ) {
// return 0;
// }
// return -1; //升序
return Long.compare(o.sumFlow,this.sumFlow);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
mapper 类
package com.compare;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CompareMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,FlowBean,Text> {
private Text phone =new Text();
private FlowBean flow = new FlowBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, Text>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//一行数据
String line = value.toString();
//切分
String[] fields = line.split("\t");
//封装
phone.set(fields[0]);
flow.setUpFlow(Long.parseLong(fields[1]));
flow.setDownFlow(Long.parseLong(fields[2]));
flow.setSumFlow(Long.parseLong(fields[3]));
//写到上下文
context.write(flow,phone);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Reducer 类
package com.compare;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
//收的数据为 流量key 手机号value 输出为 手机key 流量value
public class CompareReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean, Text,Text,FlowBean> {
/**
* Reduce收到的数据已经排完序了 我们只需要将键和值 反着输出到文件中就可以
* @param key
* @param values
* @param context
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(FlowBean key, Iterable<Text> values, Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(value,key);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
驱动类
package com.compare;
import com.partitioner.MyPartitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CompareDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(CompareDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CompareMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CompareReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// job.setSortComparatorClass(WritableComparator.class); //默认排序
// job.setGroupingComparatorClass(WritableComparator.class); //分区排序也是使用这个Comparato类
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("file:///d:/output"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("file:///d:/output2"));
boolean completion = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(completion ? 0 : 1);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# RawComparator 排序
WritableComparable 类已经帮我实现好了 RawComparator 排序中方法 所有我们可以直接继承 WritableComparable 而不是实现 RawComparator 接口
package com.compare;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class FlowComparator extends WritableComparator {
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
FlowBean fa = (FlowBean) a;
FlowBean fb = (FlowBean) b;
return Long.compare(fb.getSumFlow(), fa.getSumFlow());
}
protected FlowComparator() {
super(FlowBean.class, true);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
驱动类要 set 为自定义后的排序类
package com.compare;
import com.partitioner.MyPartitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CompareDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(CompareDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CompareMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CompareReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// job.setSortComparatorClass(WritableComparator.class); //默认排序
// job.setGroupingComparatorClass(WritableComparator.class); //分区排序也是使用这个Comparator类
job.setSortComparatorClass(FlowComparator.class); //设置为重写的Comparator类
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("file:///d:/output"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("file:///d:/output2"));
boolean completion = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(completion ? 0 : 1);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
Mappring 类和实体类一致 但实体类中的 compareTo 因为 job 已经设置了自定义的排序类 所有不会执行实体类中的 compareTo 方法
# Combiner 合并
Combiner 是 MR 程序中 Mapper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件
Combiner 组件的父类就是 Reducer
Combiner 和 Reducer 的区别在于运行的位置
Combiner 是在每一个 MapTask 所在堆叠节点运行
Reducer 是接受全局所有 Mapper 的输出结果
Combiner 的意义就是对每一个 MapTask 的输出进行局部汇总, 以减少网络传输量
Combiner 能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑,而且 Combiner 的输出 kv 应用更 Reducer 的输入 kv 类型对应起来
总结:Combiner 就是在 MapTask 时 提前将数据分组归并 减少相同数据的分区 排序 再归并,但前提条件是合并后的数据不影响产生的结果 否则空间换取时间的做法不可取
使用 在 driver 中传入 Reducer 类启用 不影响 Reducer 的使用
job.setCombinerClass(CompareReducer.class); //提前归并分组 减少数据处理时间
# GroupingComparator 分组
GroupingComparator 是在 reduce 阶段分组来使用的,由于 reduce 阶段,如果 key 相同的一组,只取第一个 key 作为 key,迭代所有的 values。 如果 reduce 的 key 是自定义的 bean,我们只需要 bean 里面的某个属性相同就认为这样的 key 是相同的,这是我们就需要之定义 GroupCoparator 来 “欺骗” reduce 了。
实体类继承 WritableComparable 接口 实现 compareTo 方法
package com.grouping; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean> { private String orderId; private String productId; private double price; @Override public String toString() { return orderId + "\t" + productId + "\t" + price; } public String getOrderId() { return orderId; } public String getProductId() { return productId; } public void setProductId(String productId) { this.productId = productId; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public void setOrderId(String orderId) { this.orderId = orderId; } //先按订单排序再根据订单相同价格降序 @Override public int compareTo(OrderBean o) { int compare = this.orderId.compareTo(o.orderId); //比较订单号是否相同 if (compare != 0) { return compare; //不相同则返回差值 } else { return Double.compare(o.price, this.price); //相同按价格升序 } } @Override public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException { dataOutput.writeUTF(orderId); dataOutput.writeUTF(productId); dataOutput.writeDouble(price); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException { } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67mapper 封装数据到实体类中
package com.grouping; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.IOException; //封装OrderBean public class OrderMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,OrderBean, NullWritable> { private OrderBean order =new OrderBean(); //mapper封装方法 @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\t"); order.setOrderId(split[0]); order.setProductId(split[1]); order.setPrice(Double.parseDouble(split[2])); //key为一个OrderBean context.write(order,NullWritable.get()); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28比较器 继承 WritableComparator 实现类 重写 compare 和无参构造方法
package com.grouping; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; //按照订单编号对数据进行分组 public class OrderComparator extends WritableComparator { //按照相同订单进入一组进行比较 @Override public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) { OrderBean oa = (OrderBean) a; OrderBean ob = (OrderBean) b; return oa.getOrderId().compareTo(ob.getOrderId()); } protected OrderComparator() { super(OrderBean.class,true); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20Reducer 类 此时 key 为实体类 value 为 null
package com.grouping; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Iterator; //取每个订单的最高价格 public class OrderReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable,OrderBean,NullWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { Iterator<NullWritable> iterator = values.iterator(); for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { //输出当前订单组中前两个最高价格 if (iterator.hasNext()){ iterator.next(); context.write(key,NullWritable.get()); } } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23驱动类 setGroupingComparatorClass 开启分组
package com.grouping; import com.flow.FlowBean; import com.flow.FlowDriver; import com.flow.FlowMapper; import com.flow.FlowReducer; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; public class OrderDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(OrderDriver.class); job.setMapperClass(OrderMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(OrderReducer.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); job.setGroupingComparatorClass(OrderComparator.class); //分组比较器 job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("file:///d:/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("file:///d:/output")); boolean completion = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(completion ? 0 : 1); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
上面 Reducer 中获取当前订单组中前两个最高价格 利用了 shuffle 中数据序列化的特性 如果在写入到磁盘中每次输出一个值创建一个映射实体类那么效率太低下 进入 Mapper 后数据就默认内部序列化了 写入到磁盘时只需创建一次映射实体类通过序列化迭代下一个键值对改变实体类的值 这样无需多次创建实体类浪费资源
# OutputFormat 数据输出

Record 类
package com.outputformat; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; //将数据按照不包含 atguigu 的数据 分别输出到两个文件中 public class MyRecordWriter extends RecordWriter<LongWritable, Text> { FSDataOutputStream atguigu = null; FSDataOutputStream other = null; public MyRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException { Configuration configuration = job.getConfiguration();//通过job获取配置文件 FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(configuration); //通过配置文件获取文件对象 String outdir = configuration.get(FileOutputFormat.OUTDIR); //获取配置文件中的输出路径地址 atguigu = fileSystem.create(new Path(outdir + "/atguigu.log"));//拼接 other = fileSystem.create(new Path(outdir + "/other.log")); } /** * 接受键值对 并按照值的不同输出到不同文件中 * * @param key 读取的一行的偏移量 * @param value 这一行的内容 * @throws IOException * @throws InterruptedException */ @Override public void write(LongWritable key, Text value) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString() + "\n"; if (line.contains("atguigu")) {//判断此行是否包含atguigu //往atguigu文件写出数据 atguigu.write(line.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } else { //往other文件写出数据 other.write(line.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } } //关闭资源 @Override public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { IOUtils.closeStream(atguigu); IOUtils.closeStream(other); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57OutputFormat 类
package com.outputformat; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; //mapping默认输出为LongWritable, Text public class MyOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<LongWritable, Text> { //返回一个处理数据的Record Writer @Override public RecordWriter<LongWritable, Text> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException, InterruptedException { return new MyRecordWriter(job); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17driver 类
package com.outputformat; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; public class OutputDrive { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration); job.setJarByClass(OutputDrive.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(MyOutputFormat.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("d:/input")); //必须保证配置文件配置正常才能正常运行 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:/output")); boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(result ? 0 : 1); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# Reduce Join
reduce side join 是一种最简单的 join 方式,其主要思想如下: 在 map 阶段,map 函数同时读取两个文件 File1 和 File2,为了区分两种来源的 key/value 数据对,对每条数据打一个标签 > (tag), 比如:tag=0 表示来自文件 File1,tag=2 表示来自文件 File2。即:map 阶段的主要任务是对不同文件中的数据打标签。> 在 reduce 阶段,reduce 函数获取 key 相同的来自 File1 和 File2 文件的 value list, 然后对于同一个 key,对 File1 和 File2 中的数据进行 join(笛卡尔乘积)。即:reduce 阶段进行实际的连接操作.
Map端的主要工作:为来自不同表或文件的key/value对,打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后用连接字段作为 key,其余部分和新加的标志作为 value,最后进行输出。Reduce端的主要工作:在 Reduce 端以连接字段作为 key 的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将那些来源于不同文件的记录(在 Map 阶段已经打标志)分开,最后进行合并就 ok 了。- 该方法的缺点:这种方式的缺点很明显就是会造成 Map 和 Reduce 端也就是 shuffle 阶段出现大量的数据传输,效率很低。
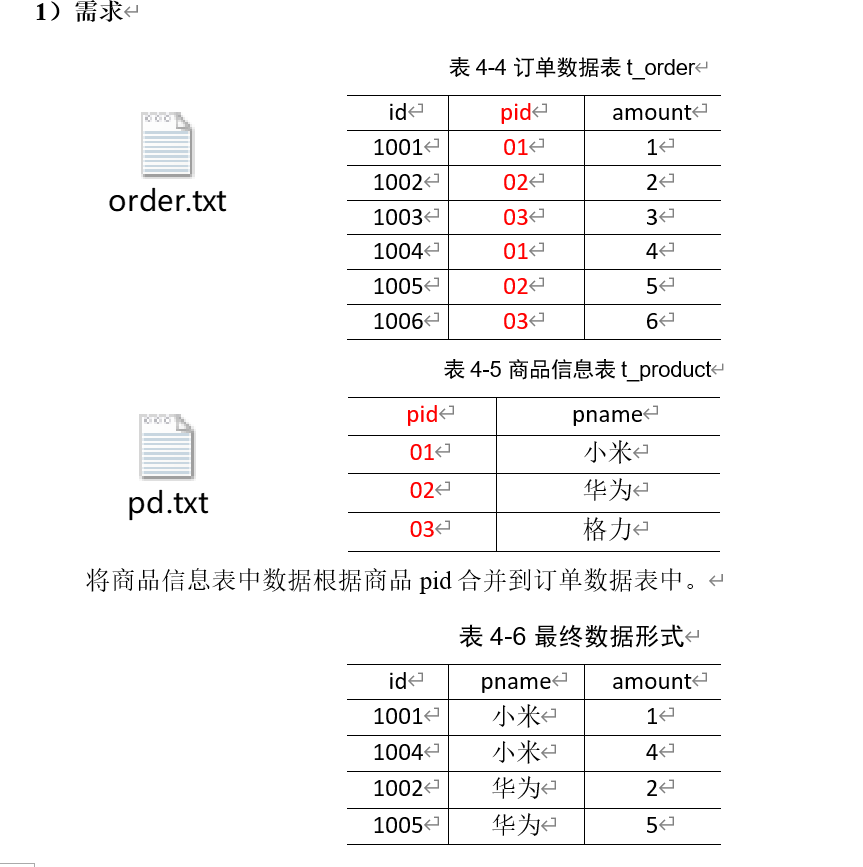
创建实体类 并排序
package com.reducejoin; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean> { private String id; private String pid; private int amount; private String pname; @Override public String toString() { return id + "\t" + pname + "\t" + amount; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getPid() { return pid; } public void setPid(String pid) { this.pid = pid; } public int getAmount() { return amount; } public void setAmount(int amount) { this.amount = amount; } public String getPname() { return pname; } public void setPname(String pname) { this.pname = pname; } @Override public int compareTo(OrderBean o) { //按pid分组 组内按照pname降序排序 int i = this.pid.compareTo(o.pid); if (i !=0){ return i; }else { return o.pname.compareTo(this.pname); } } @Override public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException { dataOutput.writeUTF(id); dataOutput.writeUTF(pid); dataOutput.writeInt(amount); dataOutput.writeUTF(pname); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException { this.id = dataInput.readUTF(); this.pid = dataInput.readUTF(); this.amount = dataInput.readInt(); this.pname = dataInput.readUTF(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80Mapper 类 根据文件名的不同来封装实体类不同的实现
package com.reducejoin; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit; import java.io.IOException; public class OrderMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable> { private OrderBean order = new OrderBean(); private String filename; //获取当前文件名 @Override protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //获取数据文件名 FileSplit fs = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit(); filename = fs.getPath().getName(); } @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\t"); //封装,按数据来源不同分别封装 if ("order.txt".equals(filename)){ //封装order order.setId(split[0]); order.setPid(split[1]); order.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(split[2])); order.setPname(""); //不能为null }else{ //封装pd order.setPid(split[0]); order.setPname(split[1]); order.setAmount(0); //不能为null order.setId(""); } context.write(order,NullWritable.get()); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44comparator 根据 pid 进行分组
package com.reducejoin; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; //分组比较器 按照order对象的pid分组 public class OrderComparator extends WritableComparator { protected OrderComparator() { super(OrderBean.class,true); } //按照pid比较a和b @Override public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) { OrderBean oa= (OrderBean) a; OrderBean ob= (OrderBean) b; return oa.getPid().compareTo(ob.getPid()); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22Reducer 进行替换合并处理好 / 标志好数据
package com.reducejoin; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Iterator; //数据替换工作 将pid换成对应的pname public class OrderReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { /*for (NullWritable value : values) { if (!"".equals(key.getPname())){ pName=key.getPname(); //遍历panme查找当前分组中有值的pname即品牌 break; //但迭代器无法进行第二次迭代遍历 }*/ //已经根据pname再次排序 并进行分组 第一个为需要的品牌名pname Iterator<NullWritable> iterator = values.iterator(); iterator.next(); String pName = key.getPname(); //获取品牌名 while (iterator.hasNext()) { iterator.next(); key.setPname(pName); //替换为对应的品牌名 context.write(key, NullWritable.get()); //写出 } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33驱动类
package com.reducejoin; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; public class OrderDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(OrderDriver.class); job.setMapperClass(OrderMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(OrderReducer.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); job.setGroupingComparatorClass(OrderComparator.class); //分组比较器 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("d:/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:/output")); boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(b ? 0 : 1); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# MapJoin
Map Join 适用于一张表十分小、一张表很大的场景。在 Map 端缓存多张表,提前处理业务逻辑,这样增加 Map 端业务,减少 Reduce 端数据的压力,尽可能的减少数据倾斜。
而使用 MapJoin 只需编写 driver 和 map 类 无需编写 reduce 类 因为不涉及到 reduce 阶段 我们在 map 阶段就处理完成
driver 开启分布式缓存并传递小文件路径
package com.mapjoin; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; public class MJDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(MJDriver.class); job.setMapperClass(MJMapper.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(0); //Map端的join不需要Reduce阶段 所以设置ReduceTask数0 //添加分布式缓存可以添加多值 传递为数组 job.addCacheFile(URI.create("file:///d:/input/pd.txt")); //设置加载缓存数据 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:/input/order.txt")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:/output")); boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(b ? 0 : 1); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37mapper setup 加载分布式缓存字节流 put 到 map 集合当中 在 map 中替换和处理要处理的数据
package com.mapjoin; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.URI; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MJMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> { private Map<String, String> pMap = new HashMap<>(); private Text k = new Text(); @Override protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //读取pd.txt到pMap //开流 URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles(); //读取分布式缓存文件路径数组 FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration()); FSDataInputStream pd = fileSystem.open(new Path(cacheFiles[0])); //pd文件 //将文件按行处理 读取到pMap中 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(pd)); //将字节流转为字符流 String line; while (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line = br.readLine())) { String[] split = line.split("\t"); pMap.put(split[0], split[1]); //转为map集合 } IOUtils.closeStream(br); } //处理order.txt的数据 @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\t"); k.set(split[0] + "\t" + pMap.get(split[1]) + "\t" + split[2]); //从map中根据pid获取value替换 context.write(k,NullWritable.get()); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
- mapJoin 效率比 ReduceJoin 高
- mapJoin 因为是提前缓存数据到内存中 如果数据量庞大那么则无法使用
# 数据清洗 (ETL) 和计数器
在运行核心业务 MapReduce 程序之前,往往要先对数据进行清洗,清理掉不符合用户要求的数据。清理的过程往往只需要运行 Mapper 程序,不需要运行 Reduce 程序
创建枚举类 方便构造计数器
package com.etl; public enum ETL { PASS,FAIL }1
2
3
4
5mapper 类 在 setup 方法中构造 Counter 计数器 在 map 中通过数据清洗 计算出符合条件的条数
package com.etl; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Counter; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.IOException; public class ETLMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> { private Counter pass; private Counter fail; @Override protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // pass = context.getCounter("ETL", "PASS"); //通过上下文构造一个计数器对象 // fail = context.getCounter("ETL", "Fail"); //通过key value赋值 pass = context.getCounter(ETL.PASS); //通过上下文构造一个计数器对象 fail = context.getCounter(ETL.FAIL); //通过枚举类来构造 } //判断日志是否需要清洗 @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] splits = value.toString().split(" "); if (splits.length > 11) { context.write(value, NullWritable.get()); pass.increment(1); //计数器+1 } else { fail.increment(1); //不符合条件的计数器+1 } //此处没有作上下文写入 默认为不改变传递给reduce } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40驱动类
package com.etl; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; public class ETLDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); job.setJarByClass(ETLDriver.class); job.setMapperClass(ETLMapper.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(0); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("d:/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:/output")); boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(b ? 0 : 1); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
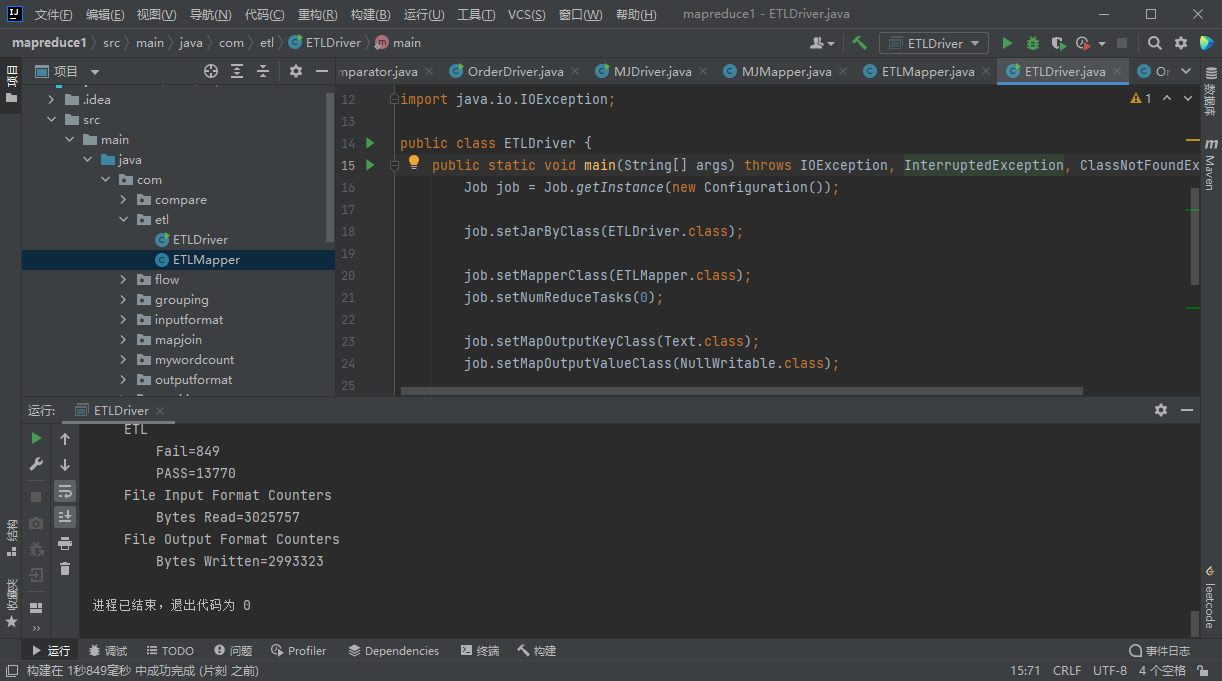
Fail 为符合条件的内容条数
PASS 为不符合条件的内容条数
# 总结
输入数据接口: InputFormat
- 默认使用的实现是: TextInputFormat
- TextInputFormat 的功能逻辑是:一次读一行文本 然后将该行的起始偏移量作为 key 行内容作为 valuie 返回
- KeyVlaueTextInputFormat 每一行均为一条记录 被分隔符分割为 key value 默认的分隔符为 \t
- NlineInputFormat 按照指定的行数 N 来划分切片
- CombineTextInputFormat 可以把多个小文件合并成一个切片处理 提高处理效率
- 用户还可以自定义 InputFormat
逻辑处理接口: Mapper
- 根据业务需求实现 map () setup cleanup () 这三个方法
Partitioner 分区
默认实现类 HashPartitioner 逻辑是根据 key 的哈希值 和 numReduces 来返回一个分区号
(key.hashCode() & Integer.MAXVALUE) % numReduces
可以自定义分区
Comparable 排序
- 当我们用自定义的对象作为 key 来输出时 必须要实现 WritableComparable 接口 重写其中的 compareTo () 方法
- 部分排序:对最终输出的每个文件进行内部排序
- 全排序:对所有数据进行排序 通常只有一个 Reduse
- 二次排序:排序的条件有两个
Combiner 合并
- Combiner 合并可以提高程序的效率,减少 IO 传输。但是使用时必须不能影响原有的业务处理结果
Reduce 端分组
- GroupingComparator 在 Reduce 端对 key 进行分组 应用于:在接收的 key 为 bean 对象时,想让一个或几个字段相同 (全部字段比较不相同) 的 key 进入到同一个 reduce 方法时,可以采用分组排序
逻辑处理接口 Reducer
- 根据业务需求实现 reduce () setup cleanup () 这三个方法
输出数据接口 OutputFormat
- 默认实现类是 TextOutputFormat 功能逻辑是 将每一个键值对 想目标文本文件输出一行
- 将 SequenceFileOutputFormat 输出作为后续 MapReduce 任务的输入,这个是一种比较好的输出格式,y 我它格式紧凑 容易被压缩
- 可以自定义 OutputFormat
