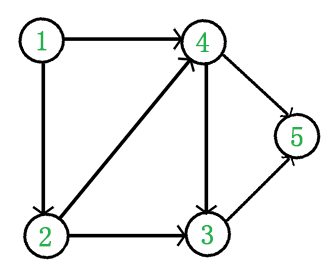
图
图
# 图
- 由点的集合和边的集合构成
- 虽然存在有向图和无向图的概念,但实际上都可以用有向图来表达
- 边上可能带有权值
# BFS
宽度优先遍历,使用队列来进行层的遍历。
- 利用队列实现
- 从源节点开始依次按宽度进队列,然后弹出
- 每弹出一个点,把该节点所有没有进过队列的邻接电放入队列
- 直到队列变空
public static void bfs(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>(); // 防止元素多次进入队列
queue.add(node);
set.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
System.out.println(cur);
for (Node next : cur.nexts) {
// 如果当前元素没有进入过队列
if (!set.contains(node)) {
set.add(next);
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# DFS
深度优先遍历,使用栈来进行深度遍历,我们可以使用递归来进行编码
- 利用栈实现
- 从源节点开始把节点按照深度放入栈,然后弹出
- 每弹出一个点,把该节点下一个没有进过栈的邻接点放入栈
- 直到栈变空
public static void dfs(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
stack.add(node);
set.add(node);
System.out.println(node.vaule);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = stack.pop();
for (Node next : cur.nexts) {
// 当前子元素没有入过栈
if (!set.contains(next)) {
stack.push(cur); // 将根元素重新入栈
stack.push(next); // 子元素同样入栈
set.add(next); // 标记为入过栈
System.out.println(next.vaule); // 输出当前子元素值
break; // 结束当前根节点的子元素遍历
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 图的拓扑排序
拓扑排序是对一个有向图构造拓扑序列,** 解决工程是否能顺利进行的问题。** 构造时有 2 种结果:
- 此图全部顶点被输出:说明说明图中无「环」存在, 是 AOV 网
- 没有输出全部顶点:说明图中有「环」存在,不是 AOV 网
AOV(Activity On Vertex Network) :一种 有向 无回路 的图
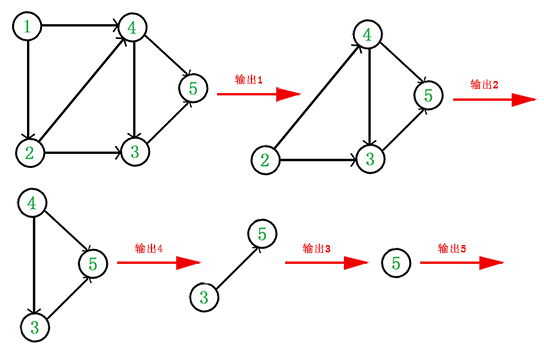
如下面的 DAG 图
- 从 DAG 图中选择一个 没有前驱(即入度为 0)的顶点并输出。
- 从图中删除该顶点和所有以它为起点的有向边。
- 重复 1 和 2 直到当前的 DAG 图为空或当前图中不存在无前驱的顶点为止。后一种情况说明有向图中必然存在环。
于是,得到拓扑排序后的结果是 {1, 2, 4, 3, 5}。
通常,一个有向无环图可以有一个或多个拓扑排序序列。
拓扑排序常用来确定一个依赖关系集中,事物发生的顺序。例如,在日常工作中,可能会将项目拆分成 A、B、C、D 四个子部分来完成,但 A 依赖于 B 和 D,C 依赖于 D。为了计算这个项目进行的顺序,可对这个关系集进行拓扑排序,得出一个线性的序列,则排在前面的任务就是需要先完成的任务。 注意:这里得到的排序并不是唯一的!就好像你早上穿衣服可以先穿上衣也可以先穿裤子,只要里面的衣服在外面的衣服之前穿就行。
如果当前节点入度为则说明此节点是首次读取,入栈并存储到结果集合中
public class Node {
public int value;
public int in; // 入度
public int out; // 出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 当前节点出发有哪些邻居节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 从当前节点出发有哪些边
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public class Edge {
public int weight; // 权重
public Node from; // 父节点
public Node to; // 子节点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;// key存储为value value存储为Node节点
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
public static List<Node> sortedTopology(Graph graph) {
// key为节点 value为剩下的入度
HashMap<Node, Integer> inMap = new HashMap<>();
// 只有剩下入度为0的点,才进入队列中
LinkedList<Node> queuq = new LinkedList<>();
for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) {
inMap.put(node, node.in); // 存储每个节点的入度
if (node.in == 0) {
// 入队列
queuq.add(node);
}
}
List<Node> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queuq.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queuq.poll();
result.add(cur);
for (Node node : cur.nexts) {
// 更新他的邻居的入度
inMap.put(node, inMap.get(node.value) - 1);
if (inMap.get(node) == 0) {
// 更新后为0 入队列
queuq.add(node);
}
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# 127・拓扑排序 (opens new window)
# DFS 解法 1
统计每个节点后面共有多少连通的节点,包括邻接节点的数量,如果两节点作比较数量较大的应该拓扑序在前,数量较小的拓扑序在后。
public static class DirectedGraphNode {
public int label;
public ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
public DirectedGraphNode(int x) {
label = x;
neighbors = new ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode>();
}
}
public static class info {
DirectedGraphNode node; //当前节点
long nodes; //当前节点连同节点的数量
public info(DirectedGraphNode node, long nodes) {
super();
this.node = node;
this.nodes = nodes;
}
}
public ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> topSort(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph) {
// key为节点 value为节点和节点数包装类
HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, info> map = new HashMap<>();
//遍历拓扑结构 得到info信息存储到map中
for (DirectedGraphNode directedGraphNode : graph) {
f(directedGraphNode, map);
}
//存储所有info信息放入集合
ArrayList<info> recordArr = new ArrayList<>();
for (info info : map.values()) {
recordArr.add(info);
}
//进行排序 节点数量多放前 少放后
Collections.sort(recordArr, new Comparator<info>() {
@Override
public int compare(info o1, info o2) {
// 无法强制成int 强转后出错
return o1.nodes == o2.nodes ? 0 : (o1.nodes > o2.nodes ? -1 : 1);
}
});
//结果集合
ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (info info2 : recordArr) {
res.add(info2.node);
}
return res;
}
// 返回当前节点 所有连同节点的个数的map
private info f(DirectedGraphNode directedGraphNode, HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, info> map) {
if (map.containsKey(directedGraphNode)) {
// 如果之前有数据 则直接取出
return map.get(directedGraphNode);
}
// 之前没算过
long nodes = 0;
for (DirectedGraphNode next : directedGraphNode.neighbors) {
nodes += f(next, map).nodes; // 递归
}
info ans = new info(directedGraphNode, nodes + 1);
// 更新存储数据
map.put(directedGraphNode, ans);
return ans;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# DFS 解法 2
我们求出每个节点的最大深度,根据每个节点的深度进行排序,深度大的放前,深度小的放后。
public static class DirectedGraphNode {
public int label;
public ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
public DirectedGraphNode(int x) {
label = x;
neighbors = new ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode>();
}
}
public static class info {
DirectedGraphNode node; // 当前节点
int deep; // 当前节点的最大深度
public info(DirectedGraphNode node, int deep) {
super();
this.node = node;
this.deep = deep;
}
}
public ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> topSort(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph) {
HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, info> map = new HashMap<>();
for (DirectedGraphNode node : graph) {
f(node, map); // 求每个节点的深度
}
ArrayList<info> recordArr = new ArrayList<>();
for (info info : map.values()) {
recordArr.add(info);
}
Collections.sort(recordArr, (o1, o2) -> (o2.deep - o1.deep));
ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (info info : recordArr) {
ans.add(info.node);
}
return ans;
}
private info f(DirectedGraphNode node, HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, info> map) {
if (map.containsKey(node)) {
// 有记录直接返回
return map.get(node);
}
int follow = 0;
for (DirectedGraphNode next : node.neighbors) {
follow = Math.max(follow, f(next, map).deep);
}
info ans = new info(node, follow + 1); // 深度加上自身
map.put(node, ans);
return ans;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# 最小生成树
# Kruskal
克鲁斯卡尔算法查找最小生成树的方法是:将连通网中所有的边按照权值大小做升序排序,从权值最小的边开始选择,只要此边不和已选择的边一起构成环路,就可以选择它组成最小生成树。对于 N 个顶点的连通网,挑选出 N-1 条符合条件的边,这些边组成的生成树就是最小生成树。
举个例子,图 1 是一个连通网,克鲁斯卡尔算法查找图 1 对应的最小生成树,需要经历以下几个步骤:
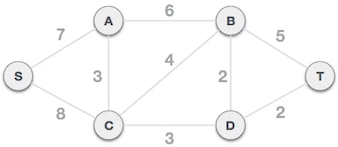
将连通网中的所有边按照权值大小做升序排序:
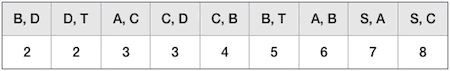
从 B-D 边开始挑选,由于尚未选择任何边组成最小生成树,且 B-D 自身不会构成环路,所以 B-D 边可以组成最小生成树。
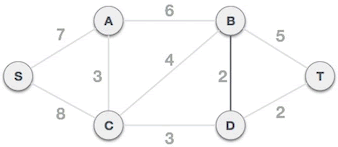
D-T 边不会和已选 B-D 边构成环路,可以组成最小生成树:
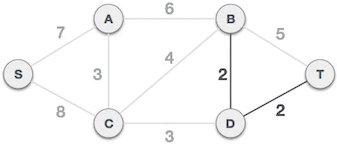
C-B 边会和已选 C-D、B-D 边构成环路,因此不能组成最小生成树:
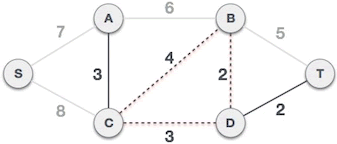
直到生成所有点 或者 权值大小集合遍历完则生成完成最小生成树
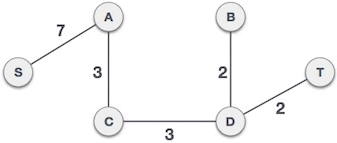
- 总是从取权值最小的边开始考虑
- 当前边要么进入最小生成树的集合,要么丢弃
- 如果当前的边进入最小生成树的集合中不会形成环,就要当前边
- 如果当前的边进入最小生成树的集合中会形成环,就不要当前边
- 考察完所有边之后,最小生成树的集合也得到了
模板写法:
- 并查集
- 权值集合最小堆 / 进行排序
- 查询当前权值的两节点是否连同如无连同则连同,并合并并查集
public class Node {
public int value;
public int in; // 入度
public int out; // 出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 当前节点出发有哪些邻居节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 从当前节点出发有哪些边
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public class Edge {
public int weight; // 权重
public Node from; // 父节点
public Node to; // 子节点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;// key存储为value value存储为Node节点
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
public static class UnionFind {
// 每个节点当前所在集合的父节点
HashMap<Node, Node> fatherMap;
// 每个节点当前所在集合的size
HashMap<Node, Integer> sizeMap;
public UnionFind() {
fatherMap = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
}
// 初始化
public void makeSet(Collection<Node> nodes) {
fatherMap.clear();
sizeMap.clear();
for (Node node : nodes) {
fatherMap.put(node, node);
sizeMap.put(node, 1);
}
}
// 查找父节点+路径压缩
public Node find(Node node) {
Stack<Node> path = new Stack<>();
while (node != fatherMap.get(node)) {
path.add(node);
node = fatherMap.get(node);
}
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
fatherMap.put(path.pop(), node);
}
return node;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Node a, Node b) {
return find(a) == find(b);
}
public void union(Node a, Node b) {
if (a == null || b == null) {
return;
}
Node f1 = find(a);
Node f2 = find(b);
if (f1 != f2) {
Integer f1Size = sizeMap.get(f1);
Integer f2Size = sizeMap.get(f2);
if (f1Size >= f2Size) {
fatherMap.put(b, a);//更新父节点
sizeMap.put(a, f1Size+f2Size); //合并大小
fatherMap.remove(b); //从并查集集合中移除合并后的节点
} else {
fatherMap.put(b, a);
sizeMap.put(b, f2Size+f1Size);
fatherMap.remove(a);
}
}
}
}
public static Set<Edge> kruskalMST(Graph graph){
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind();
unionFind.makeSet(graph.nodes.values()); //初始化并查集
//最小堆 以权值排序
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2) -> (o1.weight - o2.weight));
for (Edge edge : graph.edges) {
priorityQueue.add(edge); //加入堆中
}
Set<Edge> result = new HashSet<>();
while(!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
Edge edge = priorityQueue.poll();
//查看 from 和 to 两节点是否在一个集合中 如之前合并过则不进行操作 从堆中弹出
if(!unionFind.isSameSet(edge.from, edge.to)) {
result.add(edge); //添加到最小生成树结果集合中
unionFind.union(edge.from, edge.to); //合并两节点
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
# Prim
- 寻找图中任意点,以它为起点,它的所有边 V 加入集合 (优先队列)
q1, 设置一个boolean数组bool[]标记该位置已经确定。 - 从集合 q1 找到距离最小的那个边
v1并判断边另一点 p 是否被标记 (访问),如果p被标记说明已经确定那么跳过,如果未被标 (访问) 记那么标记该点p, 并且与 p 相连的未知点 (未被标记) 构成的边加入集合q1,边 v1 (可以进行计算距离之类,该边构成最小生成树) . - 重复 1,2 直到 q1 为空,构成最小生成树 !
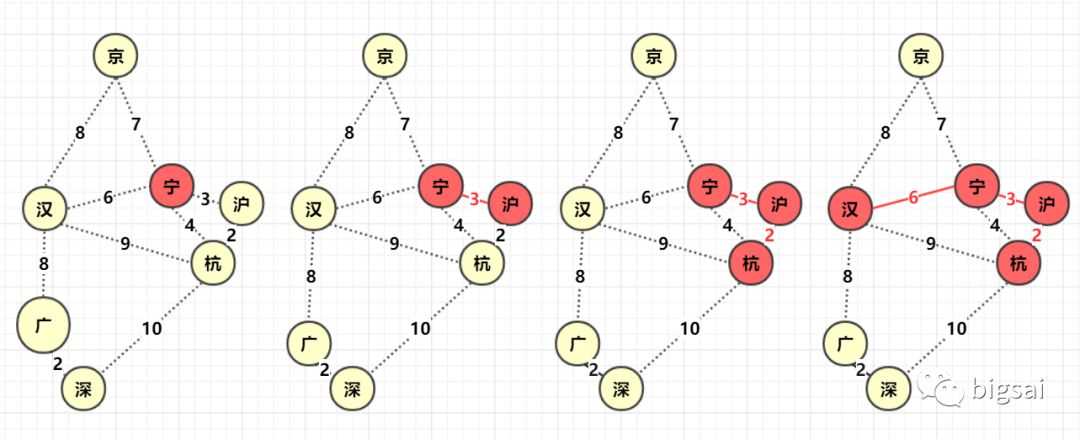
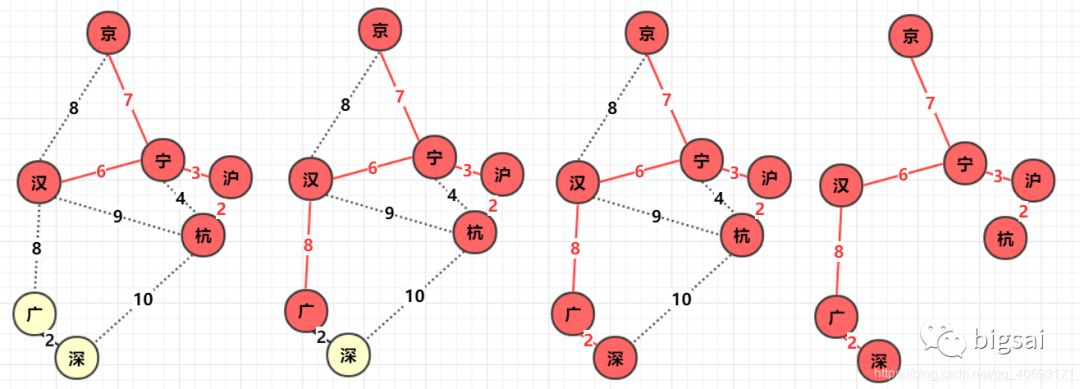
因为 prim 从开始到结束一直是一个整体在扩散,所以不需要考虑两棵树合并的问题,在这一点实现上稍微方便了一点。
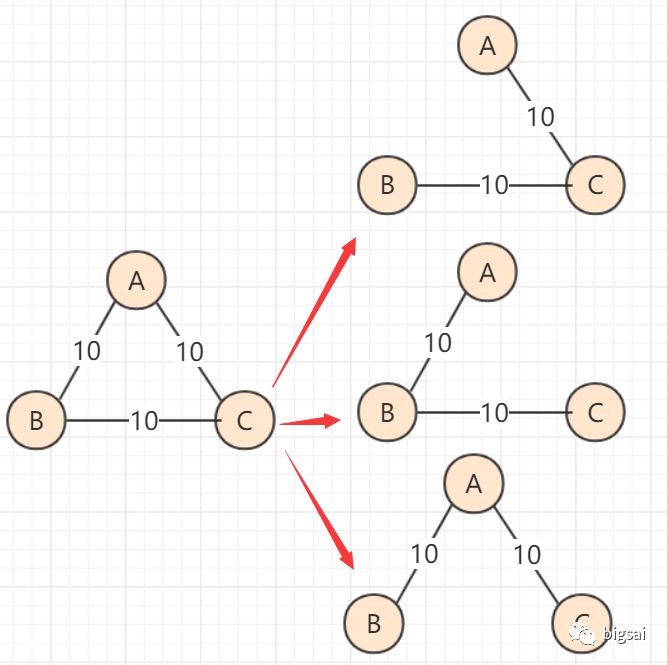
当然,要注意的是最小生成树并不唯一,甚至同一种算法生成的最小生成树都可能有所不同,但是相同的是无论生成怎样的最小生成树:
- 能够保证所有节点连通 (能够满足要求和条件)
- 能够保证所有路径之和最小 (结果和目的相同)
- 最小生成树不唯一,可能多样的如下
public class Node {
public int value;
public int in; // 入度
public int out; // 出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 当前节点出发有哪些邻居节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 从当前节点出发有哪些边
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public class Edge {
public int weight; // 权重
public Node from; // 父节点
public Node to; // 子节点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;// key存储为value value存储为Node节点
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
public static Set<Edge> primMST(Graph graph) {
// 解锁的边 放人小根堆中
PriorityQueue<Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> (o1.weight - o2.weight));
// 有哪些点被解锁过 已经被连同过的
HashSet<Node> nodeSet = new HashSet<>();
// 最小生成树节点顺序集合
HashSet<Edge> reslut = new HashSet<>();
// 从任意点开始
for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) {
// 如果当前点未被使用过
if (!nodeSet.contains(node)) {
nodeSet.add(node); // 添加到使用过的集合
// 遍历它的邻接点 加入到小根堆中
for (Edge edge : node.edges) {
queue.add(edge);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Edge edge = queue.poll(); // 弹出解锁边中 最小
Node toNode = edge.to; // 最小权值的 to节点
if (!nodeSet.contains(toNode)) { // 该节点没有被解锁过 即使用当前最小边的节点 不会形成环
nodeSet.add(toNode); // 加到解锁节点的集合
reslut.add(edge); // 结果集合
for (Edge nextEdge : toNode.edges) {
queue.add(nextEdge); // 将当前的新解锁节点的邻接节点放入小根堆中
}
}
}
}
break;
}
return reslut;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
# 单元最短路径算法 Dijkstra
狄克斯特拉算法是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是从起始点开始,采用贪心算法的策略,每次遍历到始点距离最近且未访问过的顶点的邻接节点,直到扩展到终点为止。
狄克斯特拉算法默认为无负值权值边,如果多个节点成环,并且多个权值的和为负值的会出现无法得出最短路径。
假设 v1 为源点,找从 v1 到其它节点的最短路径
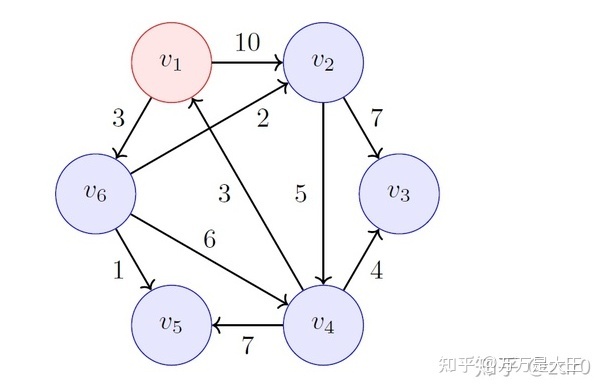
- 集合 S 用来存储已经找到的最短路径
- v1 到自己显然最短,故为初始最短路径
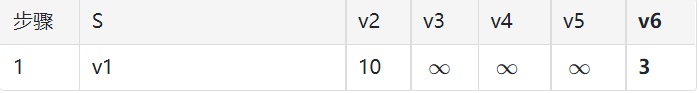
第一轮:从 v1 出发,计算 v1 到其它节点的距离(无法连接则用 “无穷” 符号)
- 全表找最小值,发现 v1 到 v6 最短为 3
- S 中添加一条最短路径:v1——v6
- v6 列标红不再考虑
第二轮:从 v1——v6 出发,计算 v1 通过 v6 到其它节点的距离
已知 v1 到 v6 为 3;v6 可以到 v2,v4,v5;因此,v1 通过 v6 到其它节点的距离为 3+n,n 为 6 到各节点的距离
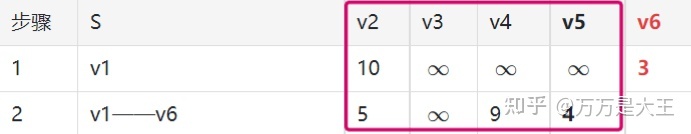
- 在全表中找最小值(v6 列已经删除),此时 4 为最小值,对应路径 v1——v6——v5
- 添加最短路径 v1——v6——v5
- v5 列不再考虑
第三轮:从 v1——v6——v5 出发,计算 v1 通过 v6 及 v5 到其它节点的距离
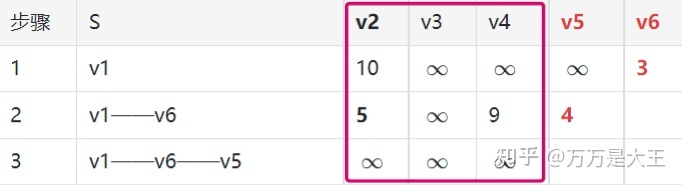
第四轮:从 v1——v6——v2 出发,计算 v1 通过 v6 及 v2 到其它节点的距离
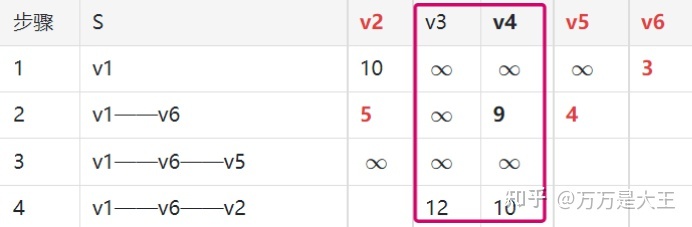
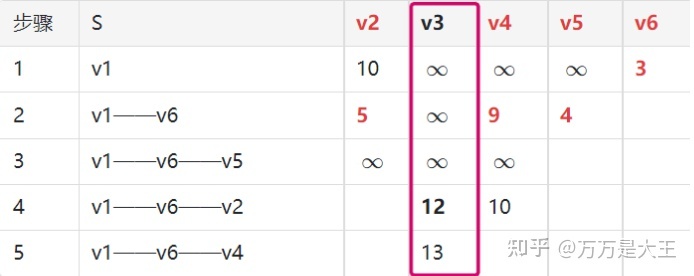
第五轮:从 v1——v6——v4 出发,计算 v1 通过 v6 及 v4 到其它节点的距离
public class Node {
public int value;
public int in; // 入度
public int out; // 出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 当前节点出发有哪些邻居节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 从当前节点出发有哪些边
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public class Edge {
public int weight; // 权重
public Node from; // 父节点
public Node to; // 子节点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;// key存储为value value存储为Node节点
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra1(Node node) {
// key为节点 value为从头节点出单源最短路径值
HashMap<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(node, 0); // 自身到自身为0
// 存储已经是最短路径的节点
HashSet<Node> selectNode = new HashSet<>();
Node minNode = getMinDistanceAndUnselectedNode(map, selectNode); // 获取没有被标记过 并且是当前单源最短路径的最小值 目前为node自身 为权值0
while (minNode != null) {
// 获取原始点 到 minNode 的最小权值距离
Integer distance = map.get(minNode);
// 遍历当前minNode所有边
for (Edge edge : minNode.edges) {
Node toNode = edge.to; // 边指向的节点
if (!map.containsKey(toNode)) {
// 说明当前指向的节点没有来过 更新为当前minNode的权值 + 当前边权值
map.put(toNode, distance + edge.weight);
} else {
// 之前有记录 查看是否能更新为最小值
map.put(toNode, Math.min(map.get(toNode), distance + edge.weight));
}
}
selectNode.add(minNode); // 查找到去往下一个节点的最短路径 将当前的出发节点 打上标记 存储到已经是最短路径的节点集合
minNode = getMinDistanceAndUnselectedNode(map, selectNode); // 获取没有被标记过 并且是当前单源最短路径的最小值的节点
}
return map;
}
public static Node getMinDistanceAndUnselectedNode(HashMap<Node, Integer> map, HashSet<Node> touchedNodes) {
Node minNode = null;
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 遍历单源最短路径节点和值 散列集合
for (Entry<Node, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Node node = entry.getKey();
Integer distance = entry.getValue();
// 如果当前节点没有被标记为过已经是最短路径 并且当前权值是最小
if (!touchedNodes.contains(node) && distance < minDistance) {
minNode = node;
minDistance = distance;
}
}
return minNode;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
# 加强堆优化
public class Node {
public int value;
public int in; // 入度
public int out; // 出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 当前节点出发有哪些邻居节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 从当前节点出发有哪些边
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public class Edge {
public int weight; // 权重
public Node from; // 父节点
public Node to; // 子节点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;// key存储为value value存储为Node节点
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
public static class NodeRecord {
Node node; // 节点
int distance; // 开始源节点到当前节点最短路径的取值和
public NodeRecord(Node node, int distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
public static class NodeHeap {
// 堆
Node[] nodes;
HashMap<Node, Integer> heapIndexMap; // 当前节点在小根堆数组的位置
HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap; // 开始源节点到当前节点最短路径的取值和
int size;
public NodeHeap(int size) {
this.size = size;
nodes = new Node[size]; // 堆数组
heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 判断当前节点是否在堆中 从索引表中查找
public boolean isEnterd(Node node) {
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
// 判断当前节点是否被标记过为最短路径了 即之前成为过堆顶并被弹出过 如被弹过索引表中记录值应为-1
public boolean inHeap(Node node) {
// 在堆中 并且没有被标记为最短路径
return isEnterd(node) && heapIndexMap.get(node) != -1;
}
// 加入堆中
public void addOrUpdateOrigonre(Node node, int dijkstra) {
// 更新节点 即存在与堆中 并且没有为标记为最短路径
if (inHeap(node)) {
// 更新为更小的权值点
distanceMap.put(node, Math.min(distanceMap.get(node), dijkstra));
}
}
// 往上移动
public void insertHeapify(int index) {
// 当前节点的权值 与 它的根节点比较大小 是否能上浮节点
while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[(index - 1) / 2])) {
swap(index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
// 下沉
public void heapify(int index, int size) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < size) {
// 查找当前节点左右孩子的最小节点 判断是否能下沉
int small = left + 1 < size && distanceMap.get(nodes[left + 1]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[left])
? left + 1
: left;
// 左右孩子的最小节点 小于 当前下标
small = distanceMap.get(nodes[small]) < distanceMap.get(index) ? small : index;
if (small == index) {
break; // 当前自身已经是最小的 无法下沉
}
swap(index, small);
index = small;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
// 弹出堆顶 最小值
public NodeRecord pop() {
// 封装节点 堆顶节点 最小路径和
NodeRecord nodeRecord = new NodeRecord(nodes[0], distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
swap(0, size - 1); // 将堆顶交换到堆数组尾部
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size - 1], -1); // 将节点的索引表更新为-1
distanceMap.remove(nodes[size - 1]); // 不再保存 当前节点的最短路径和
nodes[size - 1] = null; // 释放节点
heapify(0, --size); // 下沉交换的元素 即当前堆顶
return nodeRecord;
}
// 交换元素
private void swap(int index1, int index2) {
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index1], index2); // 更新索引表
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index2], index1);
Node temp = nodes[index1];
nodes[index1] = nodes[index2];
nodes[index2] = temp;
}
}
/**
* 加强堆实现的迪杰斯克拉算法
*
* @param head 开始源节点
* @param size 一共有多少节点
* @return 返回为散列集合 key为节点 value为从开始源节点到当前节点最短路径的取值和
*/
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra(Node head, int size) {
NodeHeap nodeHeap = new NodeHeap(size);
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrigonre(head, 0); // 源节点入加强堆 并且最短路径权值为0 自身到自身为0
HashMap<Node, Integer> result = new HashMap<>(); // key为节点 value为从源节点到自身节点的最小路径权值和
while (!nodeHeap.isEmpty()) {
NodeRecord record = nodeHeap.pop(); // 弹出堆顶
Node cur = record.node; // 当前节点
int distance = record.distance; // 当前节点的最小路径权值和
// 遍历当前节点所有邻接节点
for (Edge edge : cur.edges) {
// edge.to去往的节点 edge.weight为去往路径边的权值 要加上当前节点的最小路径和
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrigonre(edge.to, edge.weight + distance);
}
result.put(cur, distance);
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167